Hubei Ruiyuan Electronic Co.,Ltd.
Hydrogel Microneedle Patch Sensor: Rapid In Vitro Glucose Detection in Skin Interstitial Fluid
Release time:
2025-05-19
Rapid extraction and detection of biomarkers in skin interstitial fluid (ISF) using microneedles represent a key technology for real-time physiological monitoring, with significant implications for disease diagnosis and treatment.Among these, swellable hydrogel-based microneedle technology has emerged as a research hotspot in drug delivery and sensing applications due to its excellent biocompatibility and user-friendly operation.
Addressing this field, a research team from the School of Health Science and Engineering at University of Shanghai for Science and Technology and the Joint Innovation Research Institute of New Huangpu Traditional Chinese Medicine developed a crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogel microneedle patch doped with osmolytes for glucose extraction and sensing in skin interstitial fluid.The combined use of this microneedle patch with electrochemical sensors through an 'extraction-recovery-detection' workflow can be further extended to detect other biomarkers.The related research findings were published in the Journal of Transducer Technology under the title 'Hydrogel Microneedles for Rapid Interstitial Fluid Extraction Integrated with Electrochemical Sensors for In Vitro Glucose Detection'.
Swellable hydrogel microneedles are a new type of microneedle with excellent biocompatibility, requiring no additional equipment and featuring simple operation.Some crosslinked hydrogels, such as methacrylated hyaluronic acid (MeHA) and methacrylated gelatin (GelMA), exhibit high swelling ratios and can rapidly absorb large amounts of water through swelling. Therefore, they are commonly used as matrix materials for hydrogel microneedle patches to extract interstitial fluid.
In this study, to develop hydrogel microneedles capable of rapid interstitial fluid extraction for biomarker detection, researchers fabricated and characterized three types of microneedles incorporating different osmolytes using micromolding technology. These were then integrated with electrochemical sensors through an 'extraction-recovery-detection' process to create MeHA-based hydrogel microneedle patch sensors.
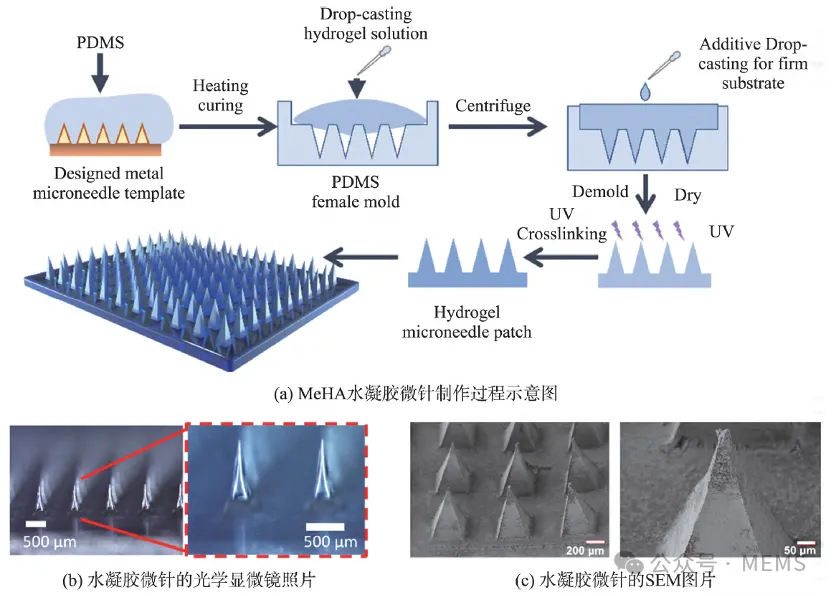
Figure 1. Fabrication and characterization of microneedles
The results demonstrate that this swellable hydrogel microneedle patch can rapidly extract (10.20 ± 2.380) μL of skin interstitial fluid within 1 min for subsequent detection.The microneedle patch was integrated with a screen-printed electrochemical sensor using an 'extraction-recovery-detection' approach, enabling glucose detection in excised porcine skin. The PB/CS/MWCNT-COOH/GOx electrode detected porcine skin glucose concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 10 mmol/L within 1 minute, with the total detection process completed in under 10 minutes.Therefore, this swellable hydrogel microneedle patch integrated with screen-printed electrochemical electrodes enables rapid extraction and detection of glucose in interstitial fluid, with potential for extension to other ISF biomarkers and real-time monitoring of physiological status.
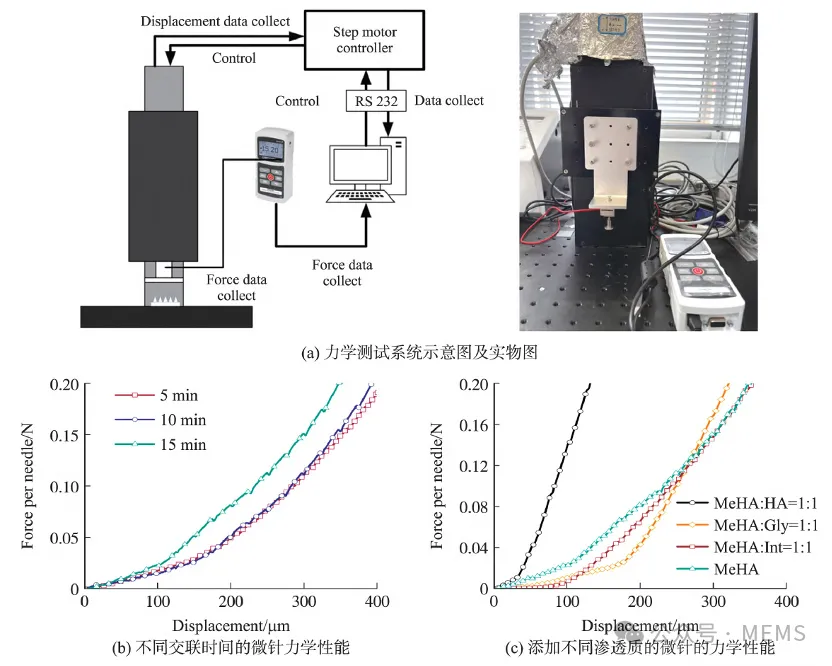
Figure 2. Mechanical testing of microneedles
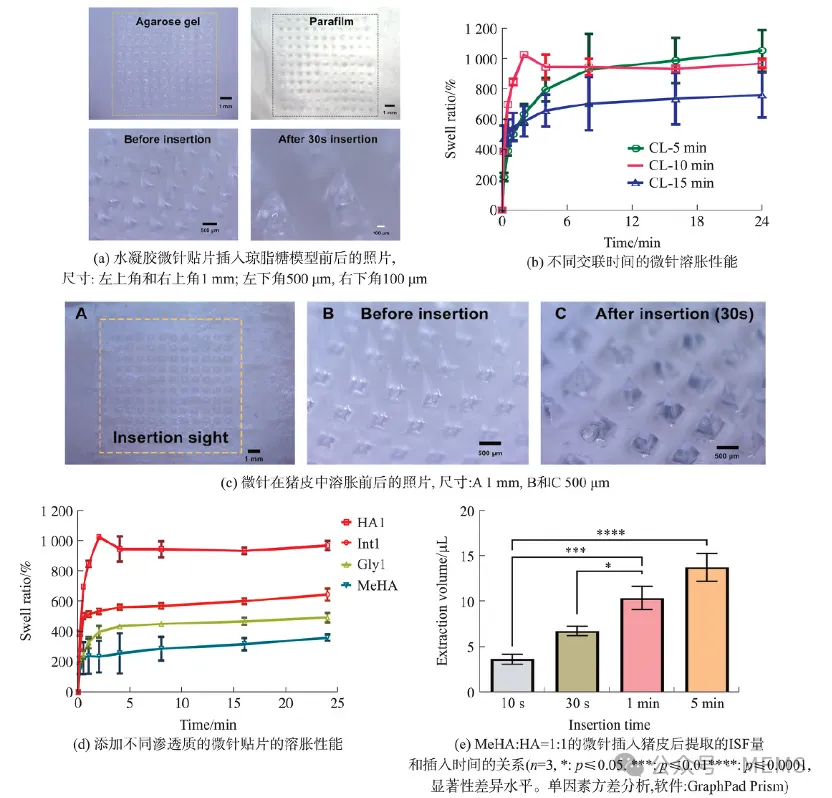
Figure 3. Swelling characterization of microneedles
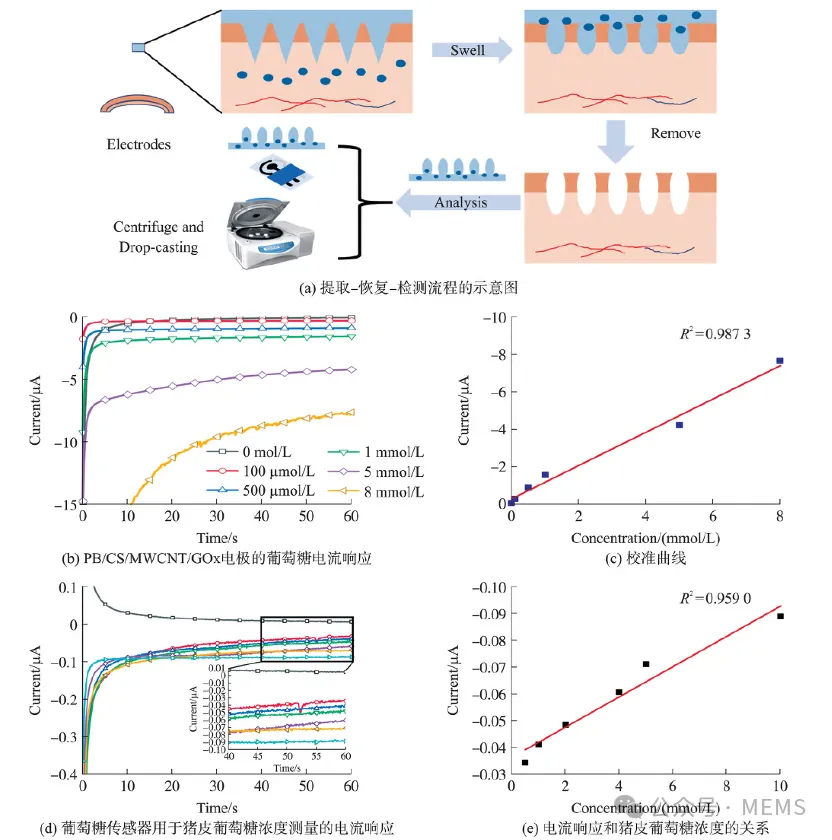
Figure 4. Integration of electrochemical sensor with hydrogel microneedle patch
This study aims to improve hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel microneedles for skin interstitial fluid extraction and explore their integration with electrochemical sensors.Compared to previous studies, this work primarily aims to enhance the interstitial fluid extraction performance of microneedle patches.Methodologically, this study employed optimized hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel microneedle patches with improved structural design and fabrication, integrated with electrochemical sensing technology for effective glucose extraction and detection in skin interstitial fluid.In the future, this microneedle can be used to build a sensor system for rapid glucose detection in skin, achieving hydrogel microneedle-based point-of-care diagnosis.
Article information:
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2025.02.002
Citation: China Electronic Components Association.
Retrieved from http://www.ic-ceca.org.cn
Online Message

